Understanding AI Capabilities and Limitations
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a pivotal element in the marketing world, offering unparalleled capabilities in data analysis, customer insights, and automation. However, it is crucial for marketers to have a realistic understanding of what AI can and cannot do to harness its full potential effectively.
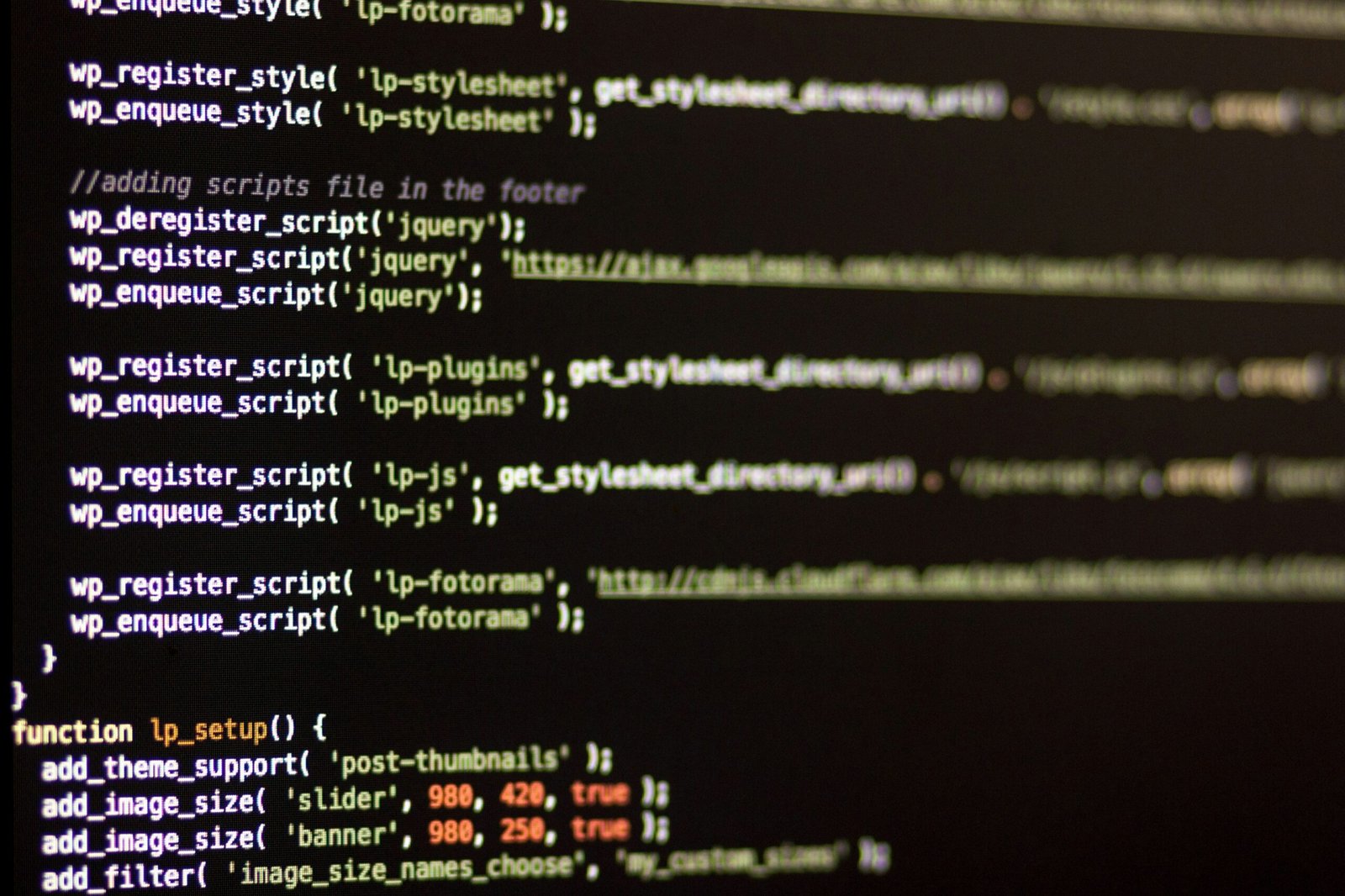
At its core, AI technology encompasses machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and data analytics. Machine learning enables systems to learn from data and improve over time without explicit programming. This is particularly useful for predictive analytics, customer segmentation, and personalized marketing strategies. Natural language processing, on the other hand, allows AI to understand, interpret, and respond to human language. This is evident in applications such as chatbots, sentiment analysis, and content generation. Data analytics, powered by AI, offers marketers the ability to process vast amounts of information quickly, providing actionable insights and optimizing decision-making processes.
Despite these advanced capabilities, AI also has its limitations. It is essential to recognize that AI operates based on the data it is fed. Poor quality data or biased datasets can lead to inaccurate predictions and flawed outcomes. Moreover, AI lacks the human touch; it cannot understand nuances, emotions, or context as a human marketer would. This limitation underscores the need for human oversight to interpret AI-driven insights correctly and apply them effectively in marketing strategies.
Successful applications of AI in marketing include personalized recommendations on e-commerce platforms, dynamic pricing strategies, and targeted advertising campaigns. For instance, Netflix uses AI to recommend shows and movies based on individual viewing history, significantly enhancing user experience and engagement. However, common pitfalls include over-reliance on AI, leading to automated decisions that may not align with brand values or customer expectations.
In conclusion, while AI offers transformative benefits, marketers must have a balanced understanding of its capabilities and limitations. By setting realistic expectations and maintaining human oversight, they can leverage AI to its fullest potential, driving innovation and achieving strategic marketing goals.
Data Quality and Management
In the realm of AI, the importance of data quality and management cannot be overstated. High-quality data is the cornerstone of effective AI tools, driving accurate insights and actionable strategies. Data accuracy, completeness, and relevance are crucial factors that determine the success of AI-driven marketing efforts. Without reliable data, even the most sophisticated AI algorithms can produce flawed outputs, leading to misguided decisions.
To ensure data quality, marketers must adopt best practices in data collection, cleaning, and management. During data collection, it is imperative to gather information from diverse and credible sources. This helps in creating a comprehensive dataset that reduces the risk of biases. Employing automated tools for data cleaning can also enhance accuracy by identifying and rectifying anomalies, duplicates, and inconsistencies. These tools streamline the process, making it more efficient and less prone to human error.
Effective data management involves organizing and storing data systematically, ensuring it is easily accessible and secure. Implementing robust data governance policies can help maintain data integrity and prevent unauthorized access. Regular audits and updates to the data repository are essential to keep the dataset current and relevant. Marketers should also consider leveraging data enrichment techniques, which augment existing data with additional information, thus providing deeper insights.
However, poor data quality poses significant risks. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to biased algorithms, resulting in skewed predictions and suboptimal marketing strategies. To mitigate these risks, marketers should continuously monitor the performance of AI models and validate their outputs against real-world scenarios. Additionally, employing fairness and transparency measures can help identify and address any biases in the data or the algorithms.
In conclusion, maintaining high data quality is fundamental for harnessing the full potential of AI in marketing. By adhering to best practices in data management and proactively mitigating risks, marketers can ensure that their AI-driven insights are both accurate and reliable, ultimately leading to more effective marketing strategies.
Personalization and Customer Experience
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way marketers approach personalization and customer experience. By leveraging AI-driven techniques such as predictive analytics, recommendation engines, and dynamic content customization, brands are able to deliver highly tailored experiences that resonate with individual customers.
Predictive analytics, for instance, harness vast amounts of data to forecast customer behaviors and preferences. This enables marketers to anticipate needs and present relevant products or services proactively. An excellent example is Netflix, which uses predictive analytics to suggest shows and movies based on viewing history. This level of personalization has significantly contributed to higher user engagement and retention rates.
Recommendation engines are another powerful tool in the AI arsenal. These engines analyze customer data to recommend products or services that align with individual tastes and preferences. Amazon has mastered this technique, using it to drive a substantial portion of its sales. By presenting customers with items they are likely to be interested in, Amazon enhances the shopping experience and increases conversion rates.
Dynamic content customization takes personalization a step further by altering content in real-time based on user behavior and attributes. For example, Spotify curates personalized playlists for its users, continually updating them with new tracks that match their musical tastes. This not only keeps users engaged but also fosters a deeper connection with the brand.
While the benefits of AI-driven personalization are clear, it is crucial to address potential privacy concerns. Customers are increasingly wary of how their data is used and stored. Brands must prioritize transparency and build trust by clearly communicating their data policies and ensuring robust data protection measures are in place. Balancing personalization with respect for customer data is essential for maintaining both customer trust and compliance with privacy regulations.
In essence, AI’s ability to enhance personalization and improve customer experiences is transforming the marketing landscape. By effectively utilizing AI techniques, brands can create more meaningful interactions, drive higher engagement, and ultimately achieve greater customer satisfaction.
Ethical Considerations and Regulatory Compliance
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to transform marketing, ethical considerations and regulatory compliance have become paramount. Marketers must navigate a complex landscape to ensure that their AI-driven strategies align with legal frameworks and ethical standards. Key areas of concern include data privacy, transparency, and algorithmic bias.
Data privacy is a critical issue in AI marketing. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States set stringent requirements for data handling. These laws mandate that companies obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting their data and provide clear information on how that data will be used. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, making it essential for marketers to implement robust data protection measures.
Transparency is another vital aspect of ethical AI use. Consumers have the right to know when AI is being used to make decisions that affect them. Marketers should strive for transparency by clearly communicating the role of AI in their processes and ensuring that AI-generated content and decisions are easily understandable. This can help build trust and foster positive relationships with customers.
Algorithmic bias presents a significant ethical challenge. AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Marketers must take proactive steps to identify and mitigate bias in their AI models. This involves regularly auditing AI systems, using diverse and representative datasets, and incorporating fairness checks into the development process.
Real-world examples illustrate the importance of ethical AI use. For instance, a major retailer faced backlash after its AI-driven recruitment tool was found to favor male candidates over female ones. In response, the company revamped its AI system to eliminate gender bias and enhance fairness. Such cases highlight the need for ongoing vigilance and accountability in AI practices.
By prioritizing ethical considerations and regulatory compliance, marketers can harness the power of AI while safeguarding consumer rights and maintaining public trust. Ensuring fairness, accountability, and transparency in AI applications is not just a legal obligation but also a strategic imperative in today’s AI-driven marketing landscape.